Abstract
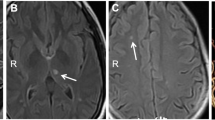
Type IV collagen α1 and α2 chains form heterotrimers that constitute an essential component of basement membranes. Mutations in COL4A1, encoding the α1 chain, cause a multisystem disease with prominent cerebrovascular manifestations, including porencephaly, bleeding-prone cerebral small vessel disease, and intracranial aneurysms. Mutations in COL4A2 have only been reported in a few porencephaly families so far. Herein, we report on a young adult patient with recurrent intracerebral hemorrhage, leukoencephalopathy, intracranial aneurysms, nephropathy, and myopathy associated with a novel COL4A2 mutation. We extensively investigated a 29-year-old male patient with recurrent deep intracerebral hemorrhages causing mild motor and sensory hemisyndromes. Brain MRI showed deep intracerebral hemorrhages of different age, diffuse leukoencephalopathy, multiple cerebral microbleeds and small aneurysms of the carotid siphon bilaterally. Laboratory work-up revealed significant microscopic hematuria and elevation of creatine-kinase. Genetic testing found a de novo glycine mutation within the COL4A2 triple helical domain. The presented case completes the spectrum of cerebral and systemic manifestations of COL4A2 mutations that appears to be very similar to that in COL4A1 mutations. Therefore, we emphasize the importance of screening both COL4A1 and COL4A2 in patients showing recurrent intracerebral hemorrhage of unknown etiology, particularly if associated with leukoencephalopathy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuo DS, Labelle-Dumais C, Gould DB (2012) COL4A1 and COL4A2 mutations and disease: insights into pathogenic mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Hum Mol Genet 21:R97–R110
Vahedi K, Alamowitch S (2011) Clinical spectrum of type IV collagen (COL4A1) mutations: a novel genetic multisystem disease. Curr Opin Neurol 24:63–68
Gould DB, Phalan FC, van Mil SE et al (2006) Role of COL4A1 in small-vessel disease and hemorrhagic stroke. N Engl J Med 354:1489–1496
Lanfranconi S, Markus HS (2010) COL4A1 mutations as a monogenic cause of cerebral small vessel disease: a systematic review. Stroke 41:e513–e518
Vahedi K, Kubis N, Boukobza M et al (2007) COL4A1 mutation in a patient with sporadic, recurrent intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 38:1461–1464
Coupry I, Sibon I, Mortemousque B, Rouanet F, Mine M, Goizet C (2010) Ophthalmological features associated with COL4A1 mutations. Arch Ophthalmol 128:483–489
Plaisier E, Gribouval O, Alamowitch S et al (2007) COL4A1 mutations and hereditary angiopathy, nephropathy, aneurysms, and muscle cramps. N Eng J Med 357:2687–2695
Verbeek E, Meuwissen ME, Verheijen FW et al (2012) COL4A2 mutation associated with familial porencephaly and small-vessel disease. Eur J Hum Genet 20:844–851
Yoneda Y, Haginoya K, Arai H et al (2012) De novo and inherited mutations in COL4A2, encoding the type IV collagen alpha2 chain cause porencephaly. Am J Hum Genet 90:86–90
Murray LS, Lu Y, Taggart A et al (2013) Chemical chaperone treatment reduces intracellular accumulation of mutant collagen IV and ameliorates the cellular phenotype of a COL4A2 mutation that causes haemorrhagic stroke. Hum Mol Genet. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddt418 [Epub ahead of print]
Jeanne M, Labelle-Dumais C, Jorgensen J et al (2012) COL4A2 mutations impair COL4A1 and COL4A2 secretion and cause hemorrhagic stroke. Am J Hum Genet 90:91–101
Acknowledgments
We thank A. Delaforge for her excellent technical help. Drs. Gunda, Kovács, Hornyák and Bereczki were supported by TÁMOP Grant No: TÁMOP-4.2.1.B-09/1/KMR.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
B. Gunda and M. Mine have contributed equally to the manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gunda, B., Mine, M., Kovács, T. et al. COL4A2 mutation causing adult onset recurrent intracerebral hemorrhage and leukoencephalopathy. J Neurol 261, 500–503 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-013-7224-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-013-7224-4