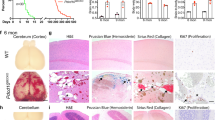
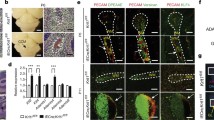
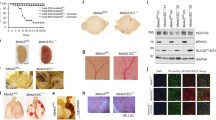
Abstract
Impairment of brain endothelial barrier integrity is critical for cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM) lesion development. The current study investigates changes in tight junction (TJ) complex organization when PDCD10 (CCM3) is mutated/depleted in human brain endothelial cells. Analysis of lesions with CCM3 mutation and brain endothelial cells transfected with CCM3 siRNA (CCM3-knockdown) showed little or no increase in TJ transmembrane and scaffolding proteins mRNA expression, but proteins levels were generally decreased. CCM3-knockdown cells had a redistribution of claudin-5 and occludin from the membrane to the cytosol with no alterations in protein turnover but with diminished protein–protein interactions with ZO-1 and ZO-1 interaction with the actin cytoskeleton. The most profound effect of CCM3 mutation/depletion was on an actin-binding protein, cortactin. CCM3 depletion caused cortactin Ser-phosphorylation, dissociation from ZO-1 and actin, redistribution to the cytosol and degradation. This affected cortical actin ring organization, TJ complex stability and consequently barrier integrity, with constant hyperpermeability to inulin. A potential link between CCM3 depletion and altered cortactin was tonic activation of MAP kinase ERK1/2. ERK1/2 inhibition increased cortactin expression and incorporation into the TJ complex and improved barrier integrity. This study highlights the potential role of CCM3 in regulating TJ complex organization and brain endothelial barrier permeability.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afridi S, Goadsby PJ (2003) New onset migraine with a brain stem cavernous angioma. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:680–682
Al-Shahi Salman R (2012) The outlook for adults with epileptic seizure(s) associated with cerebral cavernous malformations or arteriovenous malformations. Epilepsia 53(Suppl 4):34–42. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2012.03611.x
Awad IA (2012) Cavernous malformations. J Neurosurg 116:119–120. doi:10.3171/2011.6.JNS111052 (discussion 121)
Borikova AL, Dibble CF, Sciaky N, Welch CM, Abell AN, Bencharit S, Johnson GL (2010) Rho kinase inhibition rescues the endothelial cell cerebral cavernous malformation phenotype. J Biol Chem 285:11760–11764. doi:10.1074/jbc.C109.097220
Burkhardt JK, Schmidt D, Schoenauer R, Brokopp C, Agarkova I, Bozinov O, Bertalanffy H, Hoerstrup SP (2010) Upregulation of transmembrane endothelial junction proteins in human cerebral cavernous malformations. Neurosurg Focus 29:E3. doi:10.3171/2010.6.FOCUS10125
Clatterbuck RE, Eberhart CG, Crain BJ, Rigamonti D (2001) Ultrastructural and immunocytochemical evidence that an incompetent blood-brain barrier is related to the pathophysiology of cavernous malformations. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 71:188–192
Cosen-Binker LI, Kapus A (2006) Cortactin: the gray eminence of the cytoskeleton. Physiology 21:352–361. doi:10.1152/physiol.00012.2006
de Champfleur NM, Langlois C, Ankenbrandt WJ, Le Bars E, Leroy MA, Duffau H, Bonafe A, Jaffe J, Awad IA, Labauge P (2011) Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of cerebral cavernous malformations with susceptibility-weighted imaging. Neurosurgery 68:641–647. doi:10.1227/NEU.0b013e31820773cf (discussion 647–648)
Dibble CF, Horst JA, Malone MH, Park K, Temple B, Cheeseman H, Barbaro JR, Johnson GL, Bencharit S (2010) Defining the functional domain of programmed cell death 10 through its interactions with phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate. PLoS One 5:e11740. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011740
Draheim KM, Li X, Zhang R, Fisher OS, Villari G, Boggon TJ, Calderwood DA (2015) CCM2-CCM3 interaction stabilizes their protein expression and permits endothelial network formation. J Cell Biol 208:987–1001. doi:10.1083/jcb.201407129
Fanning AS, Anderson JM (2009) Zonula occludens-1 and -2 are cytosolic scaffolds that regulate the assembly of cellular junctions. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1165:113–120. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04440.x
Fauth C, Rostasy K, Rath M, Gizewski E, Lederer AG, Sure U, Zschocke J, Felbor U (2015) Highly variable intrafamilial manifestations of a CCM3 mutation ranging from acute childhood cerebral haemorrhage to late-onset meningiomas. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 128:41–43. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2014.10.023
Flemming KD, Brown RD, Link MJ (2015) Seasonal variation in hemorrhage and focal neurologic deficit due to intracerebral cavernous malformations. J Clin Neurosci. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2015.01.007
Frischer JM, Pipp I, Stavrou I, Trattnig S, Hainfellner JA, Knosp E (2008) Cerebral cavernous malformations: congruency of histopathological features with the current clinical definition. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79:783–788. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2007.132316
Garcia-Ponce A, Citalan-Madrid AF, Velazquez-Avila M, Vargas-Robles H, Schnoor M (2015) The role of actin-binding proteins in the control of endothelial barrier integrity. Thromb Haemost 113:20–36. doi:10.1160/TH14-04-0298
Gault J, Sarin H, Awadallah NA, Shenkar R, Awad IA (2004) Pathobiology of human cerebrovascular malformations: basic mechanisms and clinical relevance. Neurosurgery 55:1–16 (discussion 16–17)
Glading A, Han J, Stockton RA, Ginsberg MH (2007) KRIT-1/CCM1 is a Rap1 effector that regulates endothelial cell cell junctions. J Cell Biol 179:247–254. doi:10.1083/jcb.200705175
Han SP, Gambin Y, Gomez GA, Verma S, Giles N, Michael M, Wu SK, Guo Z, Johnston W, Sierecki E et al (2014) Cortactin scaffolds Arp2/3 and WAVE2 at the epithelial zonula adherens. J Biol Chem 289:7764–7775. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.544478
He Y, Zhang H, Yu L, Gunel M, Boggon TJ, Chen H, Min W (2010) Stabilization of VEGFR2 signaling by cerebral cavernous malformation 3 is critical for vascular development. Sci Signal 3:ra26 doi:10.1126/scisignal.2000722
Helwani FM, Kovacs EM, Paterson AD, Verma S, Ali RG, Fanning AS, Weed SA, Yap AS (2004) Cortactin is necessary for E-cadherin-mediated contact formation and actin reorganization. J Cell Biol 164:899–910. doi:10.1083/jcb.200309034
Hilder TL, Malone MH, Bencharit S, Colicelli J, Haystead TA, Johnson GL, Wu CC (2007) Proteomic identification of the cerebral cavernous malformation signaling complex. J Proteome Res 6:4343–4355. doi:10.1021/pr0704276
Hwang J, Pallas DC (2014) STRIPAK complexes: structure, biological function, and involvement in human diseases. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 47:118–148. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2013.11.021
Jakimovski D, Schneider H, Frei K, Kennes LN, Bertalanffy H (2014) Bleeding propensity of cavernous malformations: impact of tight junction alterations on the occurrence of overt hematoma. J Neurosurg 121:613–620. doi:10.3171/2014.6.JNS132775
Jensen EC (2013) Quantitative analysis of histological staining and fluorescence using ImageJ. Anat Rec 296:378–381. doi:10.1002/ar.22641
Katsube T, Takahisa M, Ueda R, Hashimoto N, Kobayashi M, Togashi S (1998) Cortactin associates with the cell-cell junction protein ZO-1 in both Drosophila and mouse. J Biol Chem 273:29672–29677
Kazakoff PW, McGuire TR, Hoie EB, Cano M, Iversen PL (1995) An in vitro model for endothelial permeability: assessment of monolayer integrity. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 31:846–852. doi:10.1007/BF02634568
Kean MJ, Ceccarelli DF, Goudreault M, Sanches M, Tate S, Larsen B, Gibson LC, Derry WB, Scott IC, Pelletier L et al (2011) Structure-function analysis of core STRIPAK Proteins: a signaling complex implicated in Golgi polarization. J Biol Chem 286:25065–25075. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.214486
Kelley LC, Hayes KE, Ammer AG, Martin KH, Weed SA (2010) Cortactin phosphorylated by ERK1/2 localizes to sites of dynamic actin regulation and is required for carcinoma lamellipodia persistence. PLoS One 5:e13847. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0013847
Kelley LC, Hayes KE, Ammer AG, Martin KH, Weed SA (2011) Revisiting the ERK/Src cortactin switch. Commun Integr Biol 4:205–207. doi:10.4161/cib.4.2.14420
Kremerskothen J, Stolting M, Wiesner C, Korb-Pap A, van Vliet V, Linder S, Huber TB, Rottiers P, Reuzeau E, Genot E et al (2011) Zona occludens proteins modulate podosome formation and function. FASEB J 25:505–514. doi:10.1096/fj.10-155598
Krisht KM, Whitehead KJ, Niazi T, Couldwell WT (2010) The pathogenetic features of cerebral cavernous malformations: a comprehensive review with therapeutic implications. Neurosurg Focus 29:E2. doi:10.3171/2010.6.FOCUS10135
Labauge P, Denier C, Bergametti F, Tournier-Lasserve E (2007) Genetics of cavernous angiomas. Lancet Neurol 6:237–244. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70053-4
Lampugnani MG, Orsenigo F, Rudini N, Maddaluno L, Boulday G, Chapon F, Dejana E (2010) CCM1 regulates vascular-lumen organization by inducing endothelial polarity. J Cell Sci 123:1073–1080. doi:10.1242/jcs.059329
Louvi A, Chen L, Two AM, Zhang H, Min W, Gunel M (2011) Loss of cerebral cavernous malformation 3 (Ccm3) in neuroglia leads to CCM and vascular pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:3737–3742. doi:10.1073/pnas.1012617108
Maddaluno L, Rudini N, Cuttano R, Bravi L, Giampietro C, Corada M, Ferrarini L, Orsenigo F, Papa E, Boulday G et al (2013) EndMT contributes to the onset and progression of cerebral cavernous malformations. Nature 498:492–496. doi:10.1038/nature12207
Martinez-Quiles N, Ho HY, Kirschner MW, Ramesh N, Geha RS (2004) Erk/Src phosphorylation of cortactin acts as a switch on-switch off mechanism that controls its ability to activate N-WASP. Mol Cell Biol 24:5269–5280. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.12.5269-5280.2004
McDonald DA, Shenkar R, Shi C, Stockton RA, Akers AL, Kucherlapati MH, Kucherlapati R, Brainer J, Ginsberg MH, Awad IA et al (2011) A novel mouse model of cerebral cavernous malformations based on the two-hit mutation hypothesis recapitulates the human disease. Hum Mol Genet 20:211–222. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddq433
McNeil E, Capaldo CT, Macara IG (2006) Zonula occludens-1 function in the assembly of tight junctions in Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cells. Mol Biol Cell 17:1922–1932. doi:10.1091/mbc.E05-07-0650
Mikati AG, Tan H, Shenkar R, Li L, Zhang L, Guo X, Larsson HB, Shi C, Liu T, Wang Y et al (2014) Dynamic permeability and quantitative susceptibility: related imaging biomarkers in cerebral cavernous malformations. Stroke 45:598–601. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.003548
Mitic LL, Anderson JM (1998) Molecular architecture of tight junctions. Annu Rev Physiol 60:121–142. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.60.1.121
Pagenstecher A, Stahl S, Sure U, Felbor U (2009) A two-hit mechanism causes cerebral cavernous malformations: complete inactivation of CCM1, CCM2 or CCM3 in affected endothelial cells. Hum Mol Genet 18:911–918. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddn420
Paris L, Tonutti L, Vannini C, Bazzoni G (2008) Structural organization of the tight junctions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1778:646–659. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.08.004
Rao RK, Basuroy S, Rao VU, Karnaky KJ Jr, Gupta A (2002) Tyrosine phosphorylation and dissociation of occludin-ZO-1 and E-cadherin-beta-catenin complexes from the cytoskeleton by oxidative stress. Biochem J 368:471–481. doi:10.1042/BJ20011804
Ren G, Crampton MS, Yap AS (2009) Cortactin: coordinating adhesion and the actin cytoskeleton at cellular protrusions. Cell Motil Cytoskelet 66:865–873. doi:10.1002/cm.20380
Riant F, Bergametti F, Ayrignac X, Boulday G, Tournier-Lasserve E (2010) Recent insights into cerebral cavernous malformations: the molecular genetics of CCM. FEBS J 277:1070–1075. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07535.x
Riant F, Bergametti F, Fournier HD, Chapon F, Michalak-Provost S, Cecillon M, Lejeune P, Hosseini H, Choe C, Orth M et al (2013) CCM3 mutations are associated with early-onset cerebral hemorrhage and multiple meningiomas. Mol Syndromol 4:165–172. doi:10.1159/000350042
Satoh H, Zhong Y, Isomura H, Saitoh M, Enomoto K, Sawada N, Mori M (1996) Localization of 7H6 tight junction-associated antigen along the cell border of vascular endothelial cells correlates with paracellular barrier function against ions, large molecules, and cancer cells. Exp Cell Res 222:269–274. doi:10.1006/excr.1996.0034
Schafer DA (2002) Coupling actin dynamics and membrane dynamics during endocytosis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 14:76–81
Schneble HM, Soumare A, Herve D, Bresson D, Guichard JP, Riant F, Tournier-Lasserve E, Tzourio C, Chabriat H, Stapf C (2012) Antithrombotic therapy and bleeding risk in a prospective cohort study of patients with cerebral cavernous malformations. Stroke 43:3196–3199. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.668533
Schneider H, Errede M, Ulrich NH, Virgintino D, Frei K, Bertalanffy H (2011) Impairment of tight junctions and glucose transport in endothelial cells of human cerebral cavernous malformations. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 70:417–429. doi:10.1097/NEN.0b013e31821bc40e
Schnoor M, Lai FP, Zarbock A, Klaver R, Polaschegg C, Schulte D, Weich HA, Oelkers JM, Rottner K, Vestweber D (2011) Cortactin deficiency is associated with reduced neutrophil recruitment but increased vascular permeability in vivo. J Exp Med 208:1721–1735. doi:10.1084/jem.20101920
Schulz GB, Wieland E, Wustehube-Lausch J, Boulday G, Moll I, Tournier-Lasserve E, Fischer A (2015) Cerebral cavernous malformation-1 protein controls DLL4-Notch3 signaling between the endothelium and pericytes. Stroke. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.007512
Shenkar R, Venkatasubramanian PN, Zhao JC, Batjer HH, Wyrwicz AM, Awad IA (2008) Advanced magnetic resonance imaging of cerebral cavernous malformations: part I. High-field imaging of excised human lesions. Neurosurgery 63:782–789. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000325490.80694.A2 (discussion 789)
Sladojevic N, Stamatovic SM, Keep RF, Grailer JJ, Sarma JV, Ward PA, Andjelkovic AV (2014) Inhibition of junctional adhesion molecule-A/LFA interaction attenuates leukocyte trafficking and inflammation in brain ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neurobiol Dis 67:57–70. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2014.03.010
Sousa S, Cabanes D, Bougneres L, Lecuit M, Sansonetti P, Tran-Van-Nhieu G, Cossart P (2007) Src, cortactin and Arp2/3 complex are required for E-cadherin-mediated internalization of Listeria into cells. Cell Microbiol 9:2629–2643. doi:10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.00984.x
Stahl S, Gaetzner S, Voss K, Brackertz B, Schleider E, Surucu O, Kunze E, Netzer C, Korenke C, Finckh U et al (2008) Novel CCM1, CCM2, and CCM3 mutations in patients with cerebral cavernous malformations: in-frame deletion in CCM2 prevents formation of a CCM1/CCM2/CCM3 protein complex. Hum Mutat 29:709–717. doi:10.1002/humu.20712
Stamatovic SM, Keep RF, Andjelkovic AV (2008) Brain endothelial cell-cell junctions: how to “open” the blood brain barrier. Curr Neuropharmacol 6:179–192. doi:10.2174/157015908785777210
Stamatovic SM, Keep RF, Wang MM, Jankovic I, Andjelkovic AV (2009) Caveolae-mediated internalization of occludin and claudin-5 during CCL2-induced tight junction remodeling in brain endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 284:19053–19066. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.000521
Stockton RA, Shenkar R, Awad IA, Ginsberg MH (2010) Cerebral cavernous malformations proteins inhibit Rho kinase to stabilize vascular integrity. J Exp Med 207:881–896. doi:10.1084/jem.20091258
Sugden PH, McGuffin LJ, Clerk A (2013) SOcK, MiSTs, MASK and STicKs: the GCKIII (germinal centre kinase III) kinases and their heterologous protein-protein interactions. Biochem J 454:13–30. doi:10.1042/BJ20130219
Tanriover G, Sozen B, Seker A, Kilic T, Gunel M, Demir N (2013) Ultrastructural analysis of vascular features in cerebral cavernous malformations. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115:438–444. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2012.06.023
Tehrani S, Tomasevic N, Weed S, Sakowicz R, Cooper JA (2007) Src phosphorylation of cortactin enhances actin assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:11933–11938. doi:10.1073/pnas.0701077104
Tu J, Stoodley MA, Morgan MK, Storer KP (2005) Ultrastructural characteristics of hemorrhagic, nonhemorrhagic, and recurrent cavernous malformations. J Neurosurg 103:903–909. doi:10.3171/jns.2005.103.5.0903
Van Itallie CM, Anderson JM (2014) Architecture of tight junctions and principles of molecular composition. Semin Cell Dev Biol 36:157–165. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.08.011
Vandenbroucke E, Mehta D, Minshall R, Malik AB (2008) Regulation of endothelial junctional permeability. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1123:134–145. doi:10.1196/annals.1420.016
Voss K, Stahl S, Schleider E, Ullrich S, Nickel J, Mueller TD, Felbor U (2007) CCM3 interacts with CCM2 indicating common pathogenesis for cerebral cavernous malformations. Neurogenetics 8:249–256. doi:10.1007/s10048-007-0098-9
Wang W, Liu Y, Liao K (2011) Tyrosine phosphorylation of cortactin by the FAK-Src complex at focal adhesions regulates cell motility. BMC Cell Biol 12:49. doi:10.1186/1471-2121-12-49
Waschke J, Burger S, Curry FR, Drenckhahn D, Adamson RH (2006) Activation of Rac-1 and Cdc42 stabilizes the microvascular endothelial barrier. Histochem Cell Biol 125:397–406. doi:10.1007/s00418-005-0080-2
Webb BA, Jia L, Eves R, Mak AS (2007) Dissecting the functional domain requirements of cortactin in invadopodia formation. Eur J Cell Biol 86:189–206. doi:10.1016/j.ejcb.2007.01.003
Weed SA, Karginov AV, Schafer DA, Weaver AM, Kinley AW, Cooper JA, Parsons JT (2000) Cortactin localization to sites of actin assembly in lamellipodia requires interactions with F-actin and the Arp2/3 complex. J Cell Biol 151:29–40
Wisniewski JR, Mann M (2012) Consecutive proteolytic digestion in an enzyme reactor increases depth of proteomic and phosphoproteomic analysis. Anal Chem 84:2631–2637. doi:10.1021/ac300006b
Wong JH, Awad IA, Kim JH (2000) Ultrastructural pathological features of cerebrovascular malformations: a preliminary report. Neurosurgery 46:1454–1459
Yadla S, Jabbour PM, Shenkar R, Shi C, Campbell PG, Awad IA (2010) Cerebral cavernous malformations as a disease of vascular permeability: from bench to bedside with caution. Neurosurg Focus 29:E4. doi:10.3171/2010.5.FOCUS10121
Yoruk B, Gillers BS, Chi NC, Scott IC (2012) Ccm3 functions in a manner distinct from Ccm1 and Ccm2 in a zebrafish model of CCM vascular disease. Dev Biol 362:121–131. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.12.006
Zebda N, Tian Y, Tian X, Gawlak G, Higginbotham K, Reynolds AB, Birukova AA, Birukov KG (2013) Interaction of p190RhoGAP with C-terminal domain of p120-catenin modulates endothelial cytoskeleton and permeability. J Biol Chem 288:18290–18299. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.432757
Zhao J, Wei J, Mialki R, Zou C, Mallampalli RK, Zhao Y (2012) Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) regulates cortactin ubiquitination and degradation in lung epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 287:19105–19114. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.339507
Acknowledgments
We thank Adrienne Chiu for excellent technical assistance in tissue array analysis. Tissue for this study was provided by Angioma Alliance, St Joseph’s Hospital and Medical Center’s Human Specimen Procurement Service. The confocal microscopy and Laser Capture Microdissection System work was performed in the Microscopy and Image-analysis Laboratory (MIL) at the University of Michigan, Department of Cell & Developmental Biology. Fluorescence microscopy and histology slide scanning was done at Department of pathology Core Flow Cytometry Laboratory and Slide Scanning Services. This work was supported by Public Health Service Grant NS075757 from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders (A.V.A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stamatovic, S.M., Sladojevic, N., Keep, R.F. et al. PDCD10 (CCM3) regulates brain endothelial barrier integrity in cerebral cavernous malformation type 3: role of CCM3-ERK1/2-cortactin cross-talk. Acta Neuropathol 130, 731–750 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1479-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1479-z